The Science of EQ Tests: Goleman, Mayer-Salovey Models Explained
October 8, 2025 | By Isla Caldwell
Feeling overwhelmed by the sheer number of online personality quizzes? You want to understand yourself better, but how can you trust that a test is giving you a real, meaningful glimpse into your emotional world? The secret lies in science. A truly valuable EQ test isn't just a collection of random questions; it's built upon decades of rigorous psychological research. What is an EQ test that you can actually rely on?
The most respected Emotional Intelligence (EQ) assessments are grounded in well-established theoretical models. Understanding these frameworks, developed by pioneers like Daniel Goleman and the team of Peter Salovey and John D. Mayer, is the first step toward accurate self-discovery. This guide will demystify the science behind EQ, helping you choose an assessment that provides genuine insight. Ready to understand the engine behind emotional awareness? You can start your journey with a scientifically-informed test.
What is Emotional Intelligence? Understanding the Core Concept
Emotional Intelligence is the ability to perceive, use, understand, manage, and handle emotions. It's about recognizing your own feelings and those of others, using this information to guide your thinking and behavior, and managing your emotions to adapt to environments or achieve your goals. It’s the critical skillset that helps you navigate the complexities of life with greater success and fulfillment.
Beyond IQ: Why EQ Matters for Personal & Professional Success
For years, IQ was seen as the primary determinant of success. We now know that's only half the story. While IQ measures cognitive ability, EQ measures emotional capability, which profoundly impacts leadership, teamwork, and resilience. High EQ helps you manage stress, communicate effectively, and build stronger relationships, all of which are vital for thriving in both your personal life and career.
The Origins of EQ: From Concept to Scientific Discipline
The term "Emotional Intelligence" was first formally defined in a 1990 paper by psychologists Peter Salovey and John D. Mayer. However, it was psychologist and science journalist Daniel Goleman who brought the concept to the mainstream with his 1995 bestseller, Emotional Intelligence. His work synthesized existing research and presented a compelling case for why EQ was a powerful predictor of a successful and happy life.
Daniel Goleman's EQ Model: Five Key Components for Life
Goleman's model is perhaps the most widely recognized framework for Emotional Intelligence. It’s a "mixed model" because it combines emotional abilities with personality traits. He breaks EQ down into five essential components that are practical and easy to understand, making them a fantastic starting point for self-improvement.
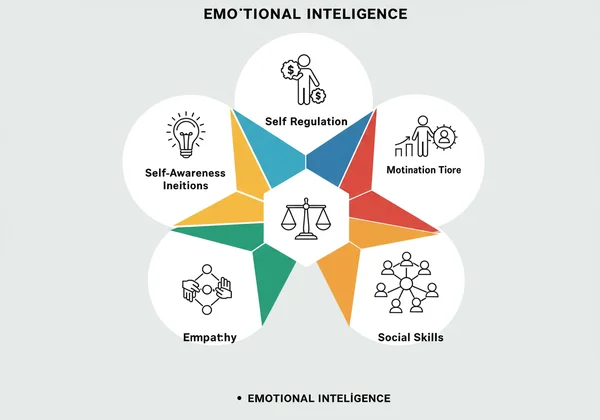
Self-Awareness: The Foundation of Emotional Intelligence
This is the cornerstone of EQ. Self-awareness is the ability to recognize and understand your own moods, emotions, and drives, as well as their effect on others. It means having a clear picture of your strengths and weaknesses and operating from a place of quiet confidence. Without knowing yourself, managing yourself becomes nearly impossible.
Self-Regulation: Managing Your Emotions Effectively
Building on self-awareness, self-regulation is the ability to control or redirect disruptive impulses and moods. It involves thinking before you act. People with strong self-regulation are less likely to make rash decisions, can manage stress effectively, and are known for their trustworthiness and integrity.
Motivation: Driving Towards Your Goals with EQ
This component refers to a passion for work and goals that goes beyond money or status. High EQ motivation is about pursuing objectives with energy and persistence. It's fueled by an internal drive for achievement, a commitment to your goals, and a readiness to seize opportunities.
Empathy: Understanding and Connecting with Others' Feelings
Empathy is the ability to understand the emotional makeup of other people. It's about treating people according to their emotional reactions, not just your own. Empathetic individuals are skilled at recognizing and responding to the unspoken feelings in a group, making them excellent team members and leaders. It's a skill you can assess when you test your EQ.
Social Skills: Navigating Relationships and Influencing Others
This is the culmination of the other components. Social skill is about managing relationships to move people in the desired direction. It encompasses a range of abilities, from effective communication and persuasion to leadership and change management. It's friendliness with a purpose: building rapport and finding common ground.
The Mayer-Salovey Four-Branch Model of Emotional Abilities
While Goleman's model is popular for its practical application, the Mayer-Salovey model is considered a more scientific "ability model." It defines EQ as a distinct mental ability, much like verbal or spatial intelligence, that can be measured objectively. It consists of four interconnected branches, moving from basic emotional perception to complex emotional management.
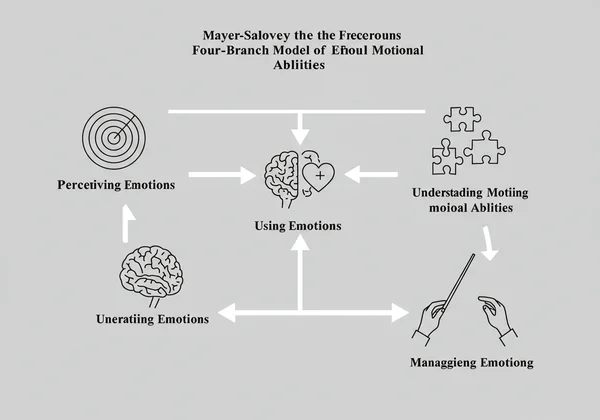
Perceiving Emotions: The First Step to Understanding
This is the most basic skill: the ability to accurately detect emotions in faces, pictures, voices, and cultural artifacts. It involves recognizing one's own emotions and those of others. Without this fundamental ability, the other branches of EQ cannot be developed.
Using Emotions: How Feelings Facilitate Thought
The second branch is the ability to harness emotions to facilitate various cognitive activities, such as thinking and problem-solving. A positive mood can foster creativity, while a sense of urgency can focus attention on critical details. This skill allows you to leverage your feelings to improve your reasoning.
Understanding Emotions: Decoding Complex Feelings
This skill involves comprehending emotional language and appreciating complex relationships among emotions. For example, it's understanding how shock can turn into grief or how admiration differs from envy. This branch is crucial for interpreting the causes of emotions and predicting how they might change over time. An accurate EQ assessment can reveal your strengths in this area.
Managing Emotions: Strategic Control for Growth
The highest level of emotional ability is managing emotions to achieve specific goals. This includes regulating your own emotions and helping others do the same. It’s about being open to feelings, both pleasant and unpleasant, and strategically using them to promote personal understanding and growth.
Beyond Theory: Integrating Models for Accurate EQ Assessment
So, which model is "better"? The truth is, they both offer invaluable perspectives. The best modern EQ tests don't strictly adhere to one model but integrate the core principles of several to provide a holistic and scientifically rigorous evaluation.

The Bar-On EQ-i 2.0 and Other Mixed Models Explained
Another influential framework is the Bar-On model, which defines emotional-social intelligence as a cross-section of interrelated competencies that determine how effectively we understand and express ourselves, relate with others, and cope with daily demands. Like Goleman's, it's a mixed model that contributes to a comprehensive view of EQ, emphasizing well-being and life satisfaction.
How Our Platform's EQ Test Methodology Aligns with Scientific Rigor
At our platform, we believe an effective EQ test must be built on a solid scientific foundation. Our assessment is carefully designed by integrating key principles from these foundational models, including Goleman's five components and the core abilities identified by Mayer and Salovey. This ensures our questions measure the multifaceted nature of emotional intelligence. After you get your EQ score, you can even opt for an AI-powered report that provides personalized, actionable insights based on these proven frameworks, turning theory into a practical plan for your growth.
Empower Your Journey: Apply Scientific EQ Understanding for Growth
Understanding the science behind Emotional Intelligence isn't just an academic exercise—it's empowering. It allows you to see EQ not as a vague, abstract concept but as a concrete set of skills that you can measure, understand, and improve. By choosing an assessment grounded in these time-tested models, you ensure that your journey of self-discovery starts on a foundation of trust and validity.
Your emotional intelligence is a powerful asset. Are you ready to measure it with a tool that respects the science? Begin your path to greater self-awareness and success today. Take our free EQ test and unlock the insights waiting within you.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is emotional intelligence and why is it important?
Emotional intelligence (EQ) is the capacity to be aware of, control, and express one's emotions, and to handle interpersonal relationships judiciously and empathetically. It's crucial because it impacts nearly every aspect of life, from decision-making and stress management to leadership and relationship success. High EQ is a strong predictor of both professional achievement and personal well-being.
What is the most accurate EQ test based on these models?
The most accurate EQ tests are those grounded in established scientific models like Goleman's or Mayer and Salovey's. Accuracy comes from a test's ability to reliably measure these defined components. While no single online quiz can be 100% definitive, a well-designed assessment provides a strong, scientifically-backed snapshot of your abilities. To see how these principles are applied, you can try a reliable test on our platform.
Can a person have high IQ but low EQ according to these theories?
Absolutely. IQ (cognitive intelligence) and EQ (emotional intelligence) are distinct sets of abilities. The theories confirm that it is entirely possible for someone to be a brilliant academic or technical expert (high IQ) but struggle with self-regulation, empathy, or social skills (low EQ). This is a classic scenario where intellectual prowess doesn't translate to life success.
How do people with high EQ behave, according to Goleman's model?
According to Goleman, people with high EQ exhibit several key behaviors. They are self-aware and understand their emotional triggers. They manage their impulses and think before they act (self-regulation). They are driven by an inner ambition (motivation), can sense and respond to others' feelings (empathy), and are skilled at building rapport and influencing others (social skills).